
This is a good way to enhance vegetable-based meals – such as in Asian-style dishes, or added to a salad. Combine nuts and seeds with low-energy dense foods (such as vegetables).Instead of snacking on a biscuit or piece of cake as a snack, have a handful of raw or dry roasted nuts.
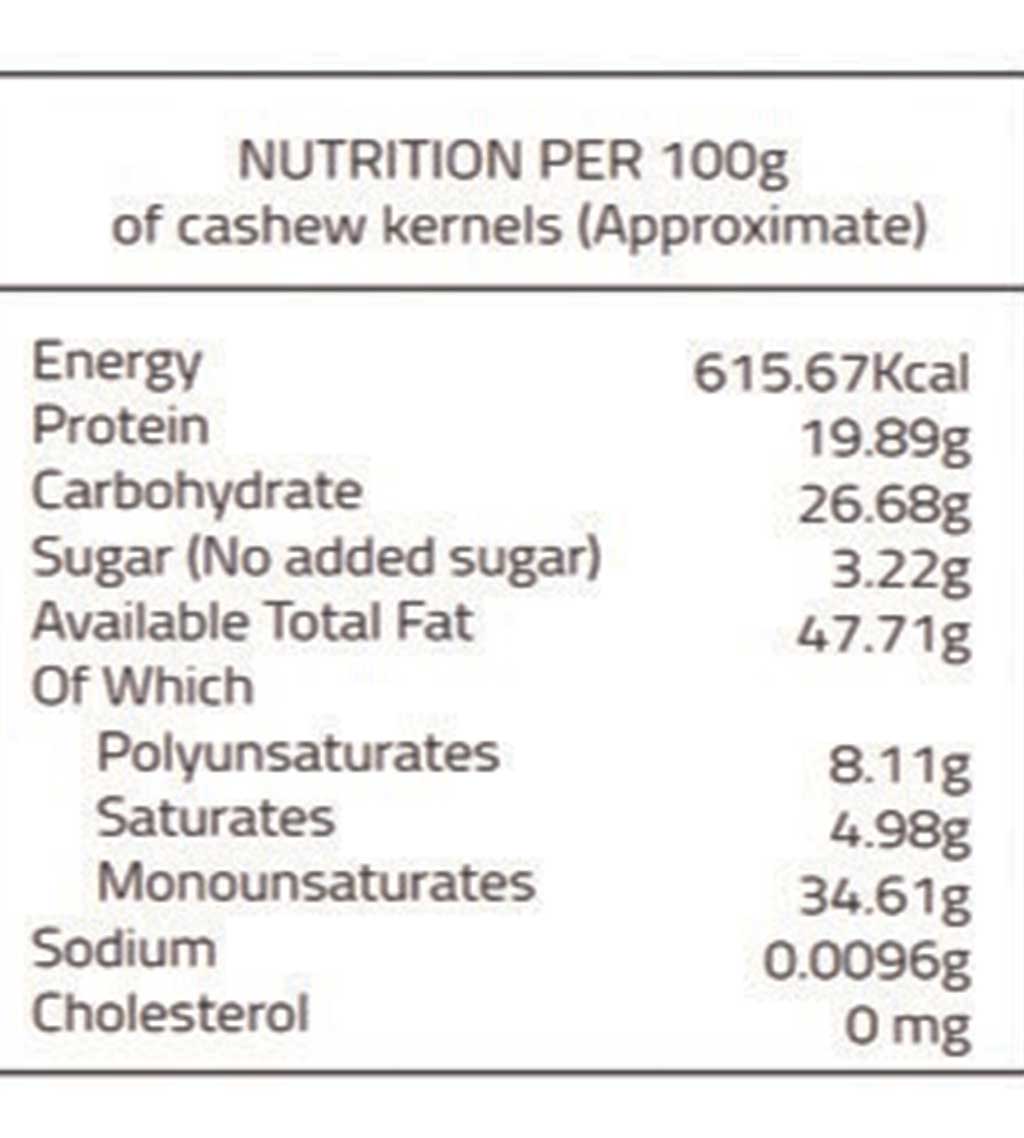
#Cashew nutrition facts per cup how to
Tips on how to make nuts and seeds a part of your diet include: Given that nuts and seeds have comparable nutrient composition and health benefits, consider seeds as a nut replacement in case of nut allergy (see information below). How to include nuts and seeds in your dietĭifferent types of nuts have slight differences in their vitamin and mineral content, so eating a variety of nuts will increase your levels of various nutrients. a small handful of peanuts or mixed nuts.One serving is approximately 30 grams – or 1/3 of a cup (or one handful). The Australian Dietary Guidelines External Link recommend 30 grams of nuts on most days of the week for adults.Īs all nuts have a similar nutrient content, a wide variety of nuts can be included as part of a healthy diet. Nuts and seeds also help to maintain healthy blood vessels and blood pressure (partly through their arginine content), and reduce inflammation in the body as they are high in antioxidants. LDL cholesterol can add to the build-up of plaque (fatty deposits) in your arteries, which can increase your risk of coronary heart disease. This combination of ‘good fats’, makes nuts heart healthy – they help to reduce low density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, (known as ‘bad’ cholesterol) in the body. Including nuts and seeds as part of your diet has been linked with a lower risk of heart disease.Īlthough high in fats, nuts and seeds are good sources of healthy fats (such as monounsaturated and polyunsaturated fats), and are low in (unhealthy) saturated fats. The effect of seeds on body weight has not been researched extensively but is likely to be similar to nuts as they are also high in protein, healthy fat and fibre. This effect is due to the protein, fat, and fibre content of nuts. As a result, food intake is reduced to compensate for the energy from nuts. Hunger and fullness – nuts help to suppress our hunger.When less fats are absorbed it means that less energy from nuts is absorbed too. Lower than expected fat absorption – fats in nuts are not fully digested and absorbed by the body.Nuts help with weight management through: The Australian Dietary Guidelines External Link recommend 30 grams of nuts on most days of the week. Therefore, nuts should be part of a healthy diet. Lower fat in the abdominal region means lower risk for chronic diseases (such as heart disease and diabetes). When included as part of a weight-loss diet, nuts have been shown to enhance weight loss and fat loss in the abdominal region.

In fact, based on large population studies, higher nut intake has been associated with lower body weight. These antioxidants have several health benefits to the human body too.ĭue to the nutrient dense characteristics of nuts and seeds, they are known to provide several health benefits, such as:Īlthough nuts and seeds are high in energy and fats, eating nuts is not connected with weight gain.
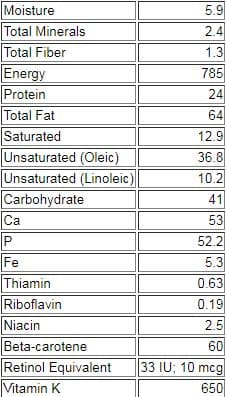
Oily seeds also contain antioxidants that stop the fats from going rancid too quickly. minerals (such as magnesium, potassium, calcium, plant iron and zinc),.protein, healthy fats (higher proportion of polyunsaturated fats) and fibre.Rich in vitamins and minerals – vitamins include E, B6, niacin and folate and minerals include magnesium, zinc, plant iron, calcium, copper, selenium, phosphorus and potassium.Rich in phytochemicals that act as antioxidants.Some nuts are also high in amino acid arginine, which keeps blood vessels healthy.Good sources of dietary protein – a good alternative to animal protein.High in ‘good fats’ External Link – monounsaturated fats (most nut types) and polyunsaturated fats (mainly walnuts).Nuts have about 29 kJ of energy per gram, and are: Common seeds include:Īll nuts have very similar macronutrient (protein, carbohydrate, and fat) profiles, but different types of nuts may have slightly different micronutrient (vitamin and mineral) content. The nutrient profiles of seeds are also very similar to those of nuts, although they tend to have a higher proportion of polyunsaturated fats than nuts. peanuts – although actually legumes, they are classified as nuts due to their similar characteristics to other tree nuts.Research shows that making nuts a regular part of a healthy diet helps to regulate our weight, and can protect against chronic diseases (such as heart disease and diabetes).Īlthough there has been limited research on seeds, they are thought to have similar health benefits to nuts due to their nutrient content which is comparable to nuts.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
